Description
| Ref. No. SS | Length | Ref. No. Ti | Length |
| 612.25 | 25mm | 612.25-Ti | 25mm |
| 612.30 | 30mm | 612.30-Ti | 30mm |
| 612.35 | 35mm | 612.35-Ti | 35mm |
| 612.40 | 40mm | 612.40-Ti | 40mm |
| 612.45 | 45mm | 612.45-Ti | 45mm |
| 612.50 | 50mm | 612.50-Ti | 50mm |
| 612.55 | 55mm | 612.55-Ti | 55mm |
| 612.60 | 60mm | 612.60-Ti | 60mm |
| 612.65 | 65mm | 612.65-Ti | 65mm |
| Ref. No. SS | Length | Ref. No. Ti | Length |
| 612.70 | 70mm | 612.70-Ti | 70mm |
| 612.75 | 75mm | 612.75-Ti | 75mm |
| 612.80 | 80mm | 612.80-Ti | 80mm |
| 612.85 | 85mm | 612.85-Ti | 85mm |
| 612.90 | 90mm | 612.90-Ti | 90mm |
| 612.95 | 95mm | 612.95-Ti | 95mm |
| 612.100 | 100mm | 612.100-Ti | 100mm |
| 612.105 | 105mm | 612.105-Ti | 105mm |
| 612.110 | 110mm | 612.110-Ti | 110mm |
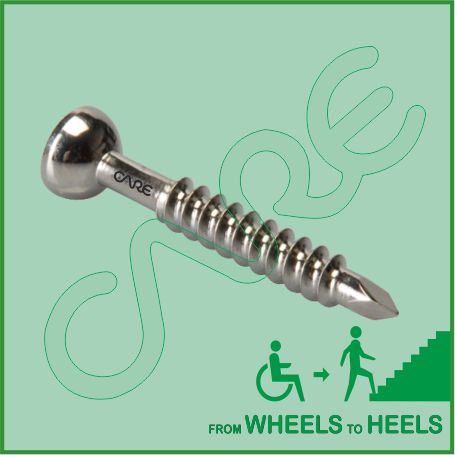
4.5mm Malleolar Screw Specification
4.5mm Malleolar Screw has a smooth shaft and is partially threaded. Malleolar Screws with cortex thread, shaft and trocar tip have limited use in the metaphyseal area, distal humerus, trochanteric area and sometimes in the ankle, where the bone is rather dense.
- 4.5mm Malleolar Screw available lengths are 25mm, 30mm, 35mm, 40mm, 45mm, 50mm, 55mm, 60mm, 65mm, 70mm, 75mm, 80mm, 85mm, 90mm, 95mm and 100mm,105mm,110mm.
- Screw has a smooth shaft and is partially threaded.
- Screws available in both Titanium and Stainless steel.
4.5mm Malleolar Screw uses
4.5mm Malleolar Screw is designed to be used for fracture fixation of small fragments in cancellous bone. It is primarily used in interfragmental compression bone plates and used in hard cortical where buttress thread form provide enhanced pull-out resistance. Hemispherical head diameter ensures optimal annular contact with washers and plates when screw is angled. Partially threaded offers best fit of threads into far bone fragment, for better interfragmentary compression.
Safe zone for the placement of medial 4.5mm Malleolar Screws
Background
Hardware placement for fracture fixation can put soft-tissue structures at risk for injury or abutment. The prominence of the hardware is a frequent cause of pain after the fixation of ankle fractures. This study was designed to assess the risk of injury or abutment of the posterior tibial tendon with the placement of medial 4.5mm Malleolar Screw.
Methods
Ten unmatched cadaveric limbs that had been disarticulated at the knee were used, and the medial malleolus was exposed by dissection of the skin. With use of fluoroscopy and direct visualization of the deep fascia, three Kirschner wires were placed through the tip of the medial malleolus and directed parallel to the medial articular surface. The first wire was placed in the center of the anterior colliculus. Two additional wires were placed parallel and posterior to the initial wire at 5-mm intervals. The wires were overdrilled, and 4.0-mm screws were inserted over the Kirschner wires. The specimens were dissected to inspect for trauma and the proximity of the screws to the posterior tibial tendon. The medial malleolus was divided into three zones on the basis of anatomic landmarks. Zone 1 is the anterior colliculus; Zone 2, the intercollicular groove; and Zone 3, the posterior colliculus.
Results
4.5mm Malleolar Screw placed in Zone 1 (the anterior colliculus) did not contact the posterior tibial tendon in any specimens. Screws placed in Zone 2 (the intercollicular groove) were, on the average, 2 mm from the posterior tibial tendon. Screws placed in Zone 3 (the posterior colliculus) resulted in tendon abutment in all ten specimens and in tendon injury in five of the ten specimens.
Conclusions
4.5mm Malleolar Screws inserted posterior to the anterior colliculus place the posterior tibial tendon at significant risk for injury or abutment.
4.5mm Malleolar Screw Precautions
- Confirm functionality of instrumentsand check for wear during reprocessing. Replace worn or damaged instruments prior to use.
- It is recommended to use the instruments identified for this 4.5mm Malleolar Screw.
- Handle devices with care and dispose worn bone cutting instruments in a sharps container.
- Always irrigate and apply suction for removal of debris potentially generated during implantation or removal.
4.5mm Malleolar Screw Warnings
- 4.5mm Malleolar Screw can break during use (when subjected to excessive forces). While the surgeon must make the final decision on removal of the broken part based on associated risk in doing so, we recommend that whenever possible and practical for the individual patient, the broken part should be removed. Be aware that implants are not as strong as native bone. Implants subjected to substantial loads may fail.
- Instruments, screws and cut plates may have sharp edges or moving joints that may pinch or tear user’s glove or skin.
- Take care to remove all fragments that are not fixated during the surgery.
- While the surgeon must make the final decision on implant removal, we recommend that whenever possible and practical for the individual patient, fixation devices should be removed once their service as an aid to healing is accomplished. Implant removal should be followed by adequate post-operative management to avoid refracture.
4.5mm Malleolar Screw General Adverse Events
As with all major surgical procedures, risks, side effects and adverse events can occur. While many possible reactions may occur, some of the most common include: Problems resulting from anesthesia and patient positioning (e.g. nausea, vomiting, dental injuries, neurological impairments, etc.), thrombosis, embolism, infection, nerve and/or tooth root damage or injury of other critical structures including blood vessels, excessive bleeding, damage to soft tissues incl. swelling, abnormal scar formation, functional impairment of the musculoskeletal system, pain, discomfort or abnormal sensation due to the presence of the device, allergy or hypersensitivity reactions, side effects associated with hardware prominence, loosening, bending, or breakage of the device, mal-union, non-union or delayed union which may lead to breakage of the implant, reoperation.
Bone screws are the most commonly used orthopedic implants. There are many different types and sizes of 4.5mm Malleolar Screw. Most bone screws are made out of stainless steel or titanium alloys. The outer diameter, root diameter, and thread pitch and angle are important in determining screw mechanics.
In orthopedics, screws are typically described by their outer diameter, for example, a “4.5mm Malleolar Screw” has an outside diameter of 4.5 mm. The pitch of a screw is the linear distance travelled by a screw for one full turn of the screw. The screw advances by a distance equal to the distance between the threads with each full turn. screws have a lower pitch and therefore more number of threads. bone screws have a greater depth of the screw to increase the surface area and therefore improve the purchase, as the bone is weaker.
Screws function by converting the tightening torque into internal tension in the screw and elastic reactions in the surrounding bone. This creates compression between the fracture fragments that the screw is holding together. 4.5mm Malleolar Screw is typically inserted into holes drilled equal to the root diameter and are either self-tapping or are inserted tapped (threaded) holes. The torque to insert cortical bone screws can be high, so the screws must be properly inserted into the correct size drilled hole and designed to withstand insertion torque levels expected in cortical bone. Malleolar bone screws have large, deep threads that grip the spongy bone well. Because of the relatively low strength of the bone, failure of the screw itself during insertion is rare, but pull out can be an issue.
 CARE IMPLANTS & INSTRUMENTS
CARE IMPLANTS & INSTRUMENTS





