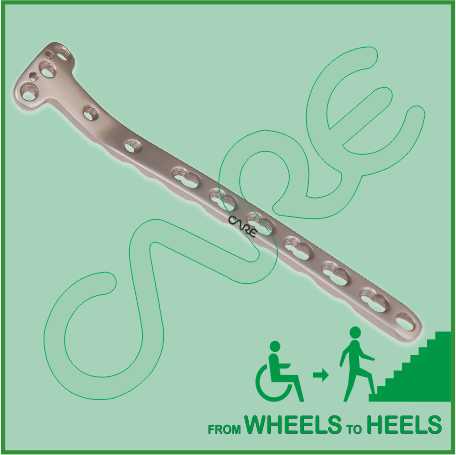
Description
| Ref. No. Ti | Ref. No. SS | Position | Size | Ref. No. Ti | Ref. No. SS | Position | Size |
| LCP681704
LCP681706 LCP681708 LCP681710 LCP681712 |
MPT-004R
MPT-006R MPT-008R MPT-010R MPT-012R |
Right
Right Right Right Right |
4H
6H 8H 10H 12H |
LCP681804
LCP681806 LCP681808 LCP681810 LCP681812 |
MPT-004L
MPT-006L MPT-008L MPT-010L MPT-012L |
Left
Left Left Left Left |
4H
6H 8H 10H 12H |
4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left Specification
- Plates available holes are 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12.
- Plates available for Left and Right both direction
- Plate has combi holes and round holes. Combi holes allow fixation with locking screws in the threaded section and cortex screws in the dynamic compression unit section for compression.
- The shaft holes accept 5 mm locking screws in the threaded portion or 4.5 mm cortical screws or 5 mm Locking cancellous screws in the compression portion. Distal locking holes in plate head accept 5 mm locking screws or 5 mm locking cancellous screws.
- 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left allow implant placement to address the individual fracture pattern.
- Two holes for preliminary fixation with K-wires, or meniscal repair with sutures in plate head.
- Limited-contact surface reduces bone-to-plate contact and helps to preserve the periosteal blood supply.
- Choice of different lengths of plate eliminates the need to cut plates.
- Pre-contoured plate to match anatomical shape.
- Available in both Titanium and Stainless steel.
- locking plate increases construct stability, decreases risk of screw back-out and subsequent loss of reduction. It also reduces the need for precise anatomic plate contouring and minimizes the risk of stripped screw holes.
- A complete Instruments Set is available for 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left. General Instruments are available for this plate such as Plate Bending Press, Plate Holding Forceps, Plate Bending Pliers, Bone Holding Forceps, Bone Elevators, Bone Cutter, Bone Nibbler, Depth Gauge, Sleeve, Screw Driver, Trocar Sleeve etc.
4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left Plate Uses
- 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left is indicated to buttress metaphyseal fractures of the medial tibial plateau, split-type fractures of the medial tibial plateau, medial split fractures with associated depressions and split or depression fractures of the medial tibial plateau.
- The plate may also be used for fixation of the proximal quarter (lateral and medial) of the tibia, as well as segmental fractures of the proximal tibia.
- The Plate may also be used for fixation of non unions and malunions of the medial proximal tibia and tibia shaft, as well as opening and closing wedge tibial osteotomies.
Advantages of using locking plate for 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left
- 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left is a locking plate so it does not have to precisely contact the underlying bone in all areas. When screws are tightened, they “lock” to the threaded screw holes of the plate, stabilizing the segments without pulling the bone to the plate. Locking screws make it impossible for screw insertion to alter the reduction. Non locking plate/screw systems require a precise adaptation of the plate to the underlying bone. Without this close contact, tightening of the screws will pull the bone segments toward the plate, resulting in loss of reduction and possibly the occlusal relationship
- Locking plate/screw systems do not disrupt the underlying cortical bone perfusion as much as conventional plates, which compress the plate to the cortical bone.
- Screws are unlikely to loosen from the plate. Similarly, if a bone graft is screwed to the plate, a locking head screw will not loosen during the phase of graft incorporation and healing. The possible advantage to this property of a locking plate/screw system is decreased risk of inflammatory complications due to hardware loosening.
- Locking plate/screw systems have been shown to provide more stable fixation than conventional non locking plate/screw systems.
Locking Screw Technology
The heads of the locking screws contain male threads while the holes in the plates contain female threads. This allows the screw head to be threaded into the 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left hole, locking the screw into the plate. This technical innovation provides the ability to create a fixed angle construct while using familiar plating techniques.
Locking Plate Technology
By using locking screws in a bone plate, a fixed-angle construct is created. In osteopenic bone or fractures with multiple fragments, secure bone purchase with conventional screws may be compromised. Locking screws do not rely on bone/plate compression to resist patient load, but function similarly to multiple small angled blade plates. In osteopenic bone or comminuted fractures, the ability to lock screws into a fixed-angle construct is imperative.
By combining locking screw holes with compression screw slots in the shaft, the plate can be used as both a locking device and a fracture compression device. If compression is desired, it must be achieved first by inserting the standard screws in the compression screw slots before inserting any locking screws.
4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left Contraindications
Contraindications may be qualified or total, and need to be taken into consideration when evaluating the prognosis in each case. Alternative management techniques may need to be considered under the following conditions:
- Acute or chronic infections, either local or systemic.
- Local or systemic accurate or chronic inflammation.
- Serve muscular, nervous or vascular disease endangering the affected area.
- Defective bone structures, which would impede adequate anchoring of the implant.
- All associated diseases which could endanger the function and success of the implant.
Warnings and Precautionary for 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left
Before using 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left, the surgeon and ancillary staff should study the safety information in these instructions, as well as any product-specific information in the product description, surgical procedures and/or brochures.
Plates are made from medical grade materials and are designed, constructed and produced with utmost care. These quality assure best working results provided they are used in the proper manner. Therefore, the following instructions for use and safety recommendations must be observed.
Improper use of Plates can lead to damage to the tissue, premature wear, destruction of the instruments and injury to the operator, patients or other persons.
It is vital for the operating surgeon to take an active role in the medical management of their patients. The surgeon should thoroughly understand all aspects of the surgical procedure and instruments including their limitations. Care in appropriate selection and proper use of surgical instruments is the responsibility of the surgeon and the surgical team. Adequate surgical training should be completed before use of this plate.
Factors which could impair the success of the operation:
- Allergies to implanted materials.
- Localized bone tumours.
- Osteoporosis or osteomalacia.
- System disease and metabolic disturbances.
- Alcohol and drug abuse.
- Physical activities involving excessive shocks, whereby the implant is exposed to blows and/or excessive loading.
- Patients who are mentally unable to understand and comply with the doctor’s instructions.
- Poor general health.
Possible Adverse Effects
The following adverse effects are the most common resulting from implantation:
- Loosening of the Medial Proximal Tibia Plate, which may result from cyclic loading of the fixation site and/or tissue reaction of the implant.
- Early and late infection.
- Further bone fracture resulting from unusual stress or weakened bone substance.
- Temporary or chronic neural damage resulting from pressure or hematomata.
- Wound hematomas and delayed wound healing.
- Vascular disease including venal thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and cardiac arrest.
- Heterotopic ossification.
- Pain and discomfort due to presence of the Implants.
- Mechanical failure of the implant, including bending, loosening or breakage.
- Migration of implant resulting in injury.
Preoperative Planning for 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left
The operating planning is carried out following a thorough clinical evaluation of the patient, Also, x-rays must be taken to allow a clear indication of the bony anatomy and associated deformities. At the time of the operation, the corresponding implantation instruments in addition to a complete set of 4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left must be available.
The clinician should discuss with the patient the possible risks and complications associated with the use of Implants. It is important to determine pre-operatively whether the patient is allergic to any of the implant materials. Also, the patient needs to be informed that the performance of the device cannot be guaranteed as complications can affect the life expectancy of the device.
4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left Precautions
- Confirm functionality of instruments and check for wear during reprocessing. Replace worn or damaged instruments prior to use.
- It is recommended to use the instruments identified for this screw.
- Handle devices with care and dispose worn bone cutting instruments in a sharps container.
- Always irrigate and apply suction for removal of debris potentially generated during implantation or removal.
4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left Warnings
- 4.5 mm Locking Medial Proximal Tibia Plate can break during use (when subjected to excessive forces). While the surgeon must make the final decision on removal of the broken part based on associated risk in doing so, we recommend that whenever possible and practical for the individual patient, the broken part should be removed. Be aware that implants are not as strong as native bone. Implants subjected to substantial loads may fail.
- Instruments, screws and cut plates may have sharp edges or moving joints that may pinch or tear user’s glove or skin.
- Take care to remove all fragments that are not fixated during the surgery.
- While the surgeon must make the final decision on implant removal, we recommend that whenever possible and practical for the individual patient, fixation devices should be removed once their service as an aid to healing is accomplished. Implant removal should be followed by adequate post-operative management to avoid refracture.
4.5 mm Locking Plate Medial Proximal Tibia, Right/Left General Adverse Events
As with all major surgical procedures, risks, side effects and adverse events can occur. While many possible reactions may occur, some of the most common include: Problems resulting from anesthesia and patient positioning (e.g. nausea, vomiting, dental injuries, neurological impairments, etc.), thrombosis, embolism, infection, nerve and/or tooth root damage or injury of other critical structures including blood vessels, excessive bleeding, damage to soft tissues incl. swelling, abnormal scar formation, functional impairment of the musculoskeletal system, pain, discomfort or abnormal sensation due to the presence of the device, allergy or hypersensitivity reactions, side effects associated with hardware prominence, loosening, bending, or breakage of the device, mal-union, non-union or delayed union which may lead to breakage of the implant, reoperation.
 CARE IMPLANTS & INSTRUMENTS
CARE IMPLANTS & INSTRUMENTS





