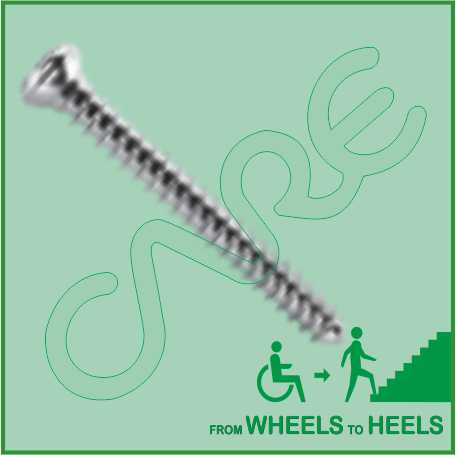
Description
| REF. NO. LENGTH
604.10 10 mm 604.12 12 mm 604.14 14 mm 604.16 16 mm 604.18 18 mm 604.20 20 mm 604.22 22 mm 604.24 24 mm 604.26 26 mm 604.28 28 mm |
REF. NO. LENGTH
604.30 30 mm 604.32 32 mm 604.34 34 mm 604.36 36 mm 604.38 38 mm 604.40 40 mm 604.45 45 mm 604.50 50 mm 604.55 55 mm 604.60 60 mm |
| Technical Specification
Thread Diameter 3.5 mm Drill Bit for Threaded Hole 2.5 mm Drill Bit for Gliding Hole 3.5 mm Core Diameter 2.4 mm Hexagonal Socket 2.5 mm Head Diameter 6.0 mm |
3.5 mm Cortex Screw Specification
- 3.5 mm Cortex Screw available lengths are 10mm, 12mm, 14mm, 16mm, 18mm, 20mm, 22mm, 24mm, 26mm, 28mm, 30mm, 32mm, 34mm, 36mm, 38mm, 40mm, 42mm, 44mm, 46mm, 48mm, 50mm, 52mm, 54mm, 56mm, 58mm and 60mm.
- 3.5 mm Cortex Screw is made from pure Titanium and SS 316L.
- Any additional length sizes of this screw will be made on demand.
- This is Self Tapping Screw. Self Tapping Screws cuts its own thread while being driven into the bone. It makes a small hole while entering the bone which creates a tight friction fit between the threads. This helps fight vibration loosening and allows the parts to be taken apart if needed..
- Instruments are available for this screw such as Bone Taps, Combined Drill & Tap Sleeve, Counter Sink, Depth Gauge, Drill Bits, Drill Guide, Drill Sleeve, Hollow Mill Screw Removal, Reverse Measuring Device, Screw Drivers and Screw Holding Forceps etc.
3.5 mm Cortex Screw uses
3.5 mm Cortex Screw is used in fixation of 3.5 mm locking plates.
Bone screws are the most commonly used orthopedic implants. There are many different types and sizes of screws for different types of bones. Most bone screws are made out of stainless steel or titanium alloys. The outer diameter, root diameter, and thread pitch and angle are important in determining screw mechanics.
In orthopedics, screws are typically described by their outer diameter, for example, a “3.5 mm Cortex Screw” has an outside diameter of 3.5 mm. The pitch of a screw is the linear distance travelled by a screw for one full turn of the screw. The screw advances by a distance equal to the distance between the threads with each full turn. Cortex screws have a lower pitch and therefore more number of threads. Cortex bone screws have a greater depth of the screw to increase the surface area and therefore improve the purchase, as the bone is weaker.
Screws function by converting the tightening torque into internal tension in the screw and elastic reactions in the surrounding bone. This creates compression between the fracture fragments that the screw is holding together. 3.5 mm Cortex Screw is typically inserted into holes drilled equal to the root diameter and are either self-tapping or are inserted tapped (threaded) holes. The torque to insert cortical bone screws can be high, so the screws must be properly inserted into the correct size drilled hole and designed to withstand insertion torque levels expected in cortical bone. Cortex bone screws have large, deep threads that grip the spongy bone well. Because of the relatively low strength of the cortex bone, failure of the screw itself during insertion is rare, but pull out can be an issue.
 CARE IMPLANTS & INSTRUMENTS
CARE IMPLANTS & INSTRUMENTS





